Li Qingzhao – Protector of History
Today I want to bring you a story of a happy marriage between two bookworms. They were collecting historical artifacts and writing each other love letters …until they lost their home and most of their beloved collection. And then her husband died too. It’s a lot. This is a story of a picture perfect life turning to ashes, but it’s also a story of resilience and protecting what we love. This is the story of Li Qingzhao.
Born around 1084 in Zhangqiu, China as the first child of a family of scholars and government officials, Qingzhao had a great start in life! Her father was the headmaster of the capital’s university and saw to it that all of his children, one boy and three girls, received a thorough education. The family seems to have been fairly progressive as the girls’ feet were not bound, a popular custom throughout China at the time. Furthermore when Qingzhao started writing in her teens, she was taken seriously by her family and encouraged to pursue her passion. And so she developed into an intelligent and outgoing young woman.
When she was 18 years old, she entered an arranged marriage with Zhao Mingcheng, who was 23 years old and a poet as well. I’m a bit confused as to why he was chosen for her, as their parents had different opinions in politics (her father was a conservative, while his father was a reformist) and they were not particularly wealthy. But it turned out to be a wonderful match. Although Mingchen was often gone for work and they were never particularly wealthy, they were very happy. Both loved history and the little money they had, they used to buy statues, paintings, calligraphies and reproductions of historical inscriptions. They would spend hours upon hours examining the pieces and cataloguing them. Whenever they could, they would write each other little love letters – with Qingzhao being the better poet. And during their tea ceremonies they would play a game in which whoever could name the origin of a quote was the one to drink first. They were very much in love.
Their happy married life took a little hit three years later, when not only Qingzhao’s father died, but so did Mingcheng’s two years later. There was some political tension involved and so the couple decided to lay low for a while and move out into the country, located in what is now Shandong Province. In favor of acquiring new artifacts, the couple lived a minimalist life and often went out themselves in search for new items for their collection. For the longer trips however, Qingzhao was left in their home and spent her time writing …and drinking a fair share. Many of her poems from that time are about loneliness and intoxication – a scandal for a woman of her status, as these topics had been reserved for prostitutes, not honorable wives! It’s not like she cared about that though.
Generally they seem to have been happy in their secluded little life though, and even when the political climate calmed down after five years in their new home, they decided to stay there. They never had any children and there is no word of that in neither her nor his writings, so I assume they didn’t really care. That’s highly unconventional as it was an important part of Chinese culture to continue the family line. Instead of doing that however, they amassed one of the most valuable collections of historical artifacts in all of China. And for nine more years, they lived a quiet life, content in each other’s company and surrounded by their biggest passion.
Until in 1121, Mingcheng was ordered to move to Laizhou to occupy a political post. Even though this time Qingzhao could come with him, it meant they had to leave their beloved home. And that wasn’t the end of it. In 1127, the capital of the Song Dynasty, Kaifeng, fell to the neighboring Jin. The government had been buying peace so far, but eventually that wasn’t enough anymore.
Although Qingzhao was advocating for a strong offense against the invaders, in the end she had no choice but pack her stuff and flee. And packing she did. With her husband, she hand-picked every little piece to take with them, ending up with fifteen (15!) carts of the most valuable artifacts in their collection. Still that meant ten more rooms (!) left behind for certain destruction.
Arriving in Nanjing, the two lovers parted ways. Mingcheng had to see to the funeral of his mother who had just died, while Qingzhao was determined to save whatever she could from their old family home in Shandong Province. Travelling against the stream of refugees, she finally reached her destination. However the Jin were fast approaching, so she had to leave with only a few pieces, seeing her beloved collection burn behind her.
After a long journey she returned to Nanjing where she was reunited with her much-missed husband. Together they travelled south on the Yangtze River to find a safe place for their prized collection. However their time together was cut short once again when Mingcheng was ordered to take a political post once again. Shortly after the lovers parted ways, he fell sick with malaria. As soon as Qingzhao heard, she left for Nanjing where he was staying. She didn’t even think about her collection that she went through so much to safe, she took off to see her husband again.
She did arrive in time to see him again before he died. According to custom it would be the eldest son writing the epitaph, but as there was no son, Qingzhao wrote Mingcheng’s. A final little love letter.
Now Qingzhao was 45. She was completely alone, homeless and didn’t even really have a solid country to return to. After burying her beloved husband with all honors, she recovered her second love, her artifacts, so at least she wasn’t broke. But once again the Jin were not far and she had to flee again. Her journey took her through all of Southern China and gradually she had to sell more and more of her collection until almost nothing was left. With all the refugees, finding her family was impossible and she had nowhere to go. After three years the new borders were finally relatively established and Qingzhao moved to the new capital of Hangzhou in Eastern China.
In the same year, just after the mourning period had passed, she apparently remarried (although this is not 100% verified.) Another highly unorthodox move as Confucianist law forbids widows from marrying again. I can only guess as to why she chose to do this. Maybe it was the longing for stability and a home, maybe the wish for another companion, someone to share her passion with. Her new husband however was not that. Not only was he far from being on her level, intellectually speaking, but it appears he also harmed her physically. Not even 100 days into marriage, Qingzhao demanded a divorce. In another unorthodox move, she took her case to court – and she won! Her ex-husband was banished and she never looked for another.
Instead she threw herself into writing. Once so outgoing and unconventional, her poems are now about her lost home, her lost love and her lost happiness. Also a lot more about drinking. But her intellect and abilities as a poet didn’t suffer and even though she seems to have become severely depressed, she didn’t give up entirely.
After five years, in 1134, she published a monumental catalogue of antique inscriptions in bronze and stone which her husband had assembled. She herself wrote the foreword (and probably helped with cataloguing too, but she never took credit.) It is still a recognized educational book on the subject. All the while she continued to write poems criticizing the Dynasty’s politics regarding the new borders. Her last known poems were written in 1143, when she was almost 60, then she vanishes from history.
It is unknown when exactly she died, but it must have been around 1155. But she isn’t forgotten. In China she remains one of the greatest poets in history, even though most of her writing has been lost to time and war. There is even a crater on Venus named after her, as well as one on Mercury! And although she couldn’t protect her collection, who knows how many pieces of Chinese history in our museums went through the hands of Li Qingzhao?!
image credits:
1: Li Qingzhao and Mingcheng Zhao (presumably), artist unknown – Link
If you happen to know the creator, please let me know, I couldn’t find them!
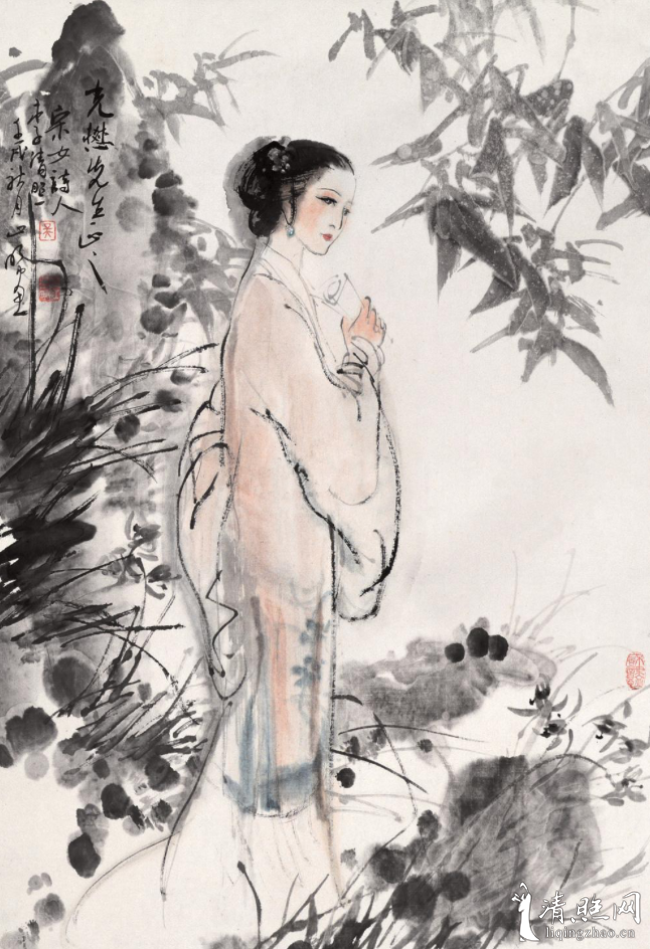
2: Li Qingzhao’s “Summer Judgment · Life as a Master” illustrated by Wang Xijing in 1990 – Link
3: Wu Shanming: “Poet Li Qingzhao” – Link
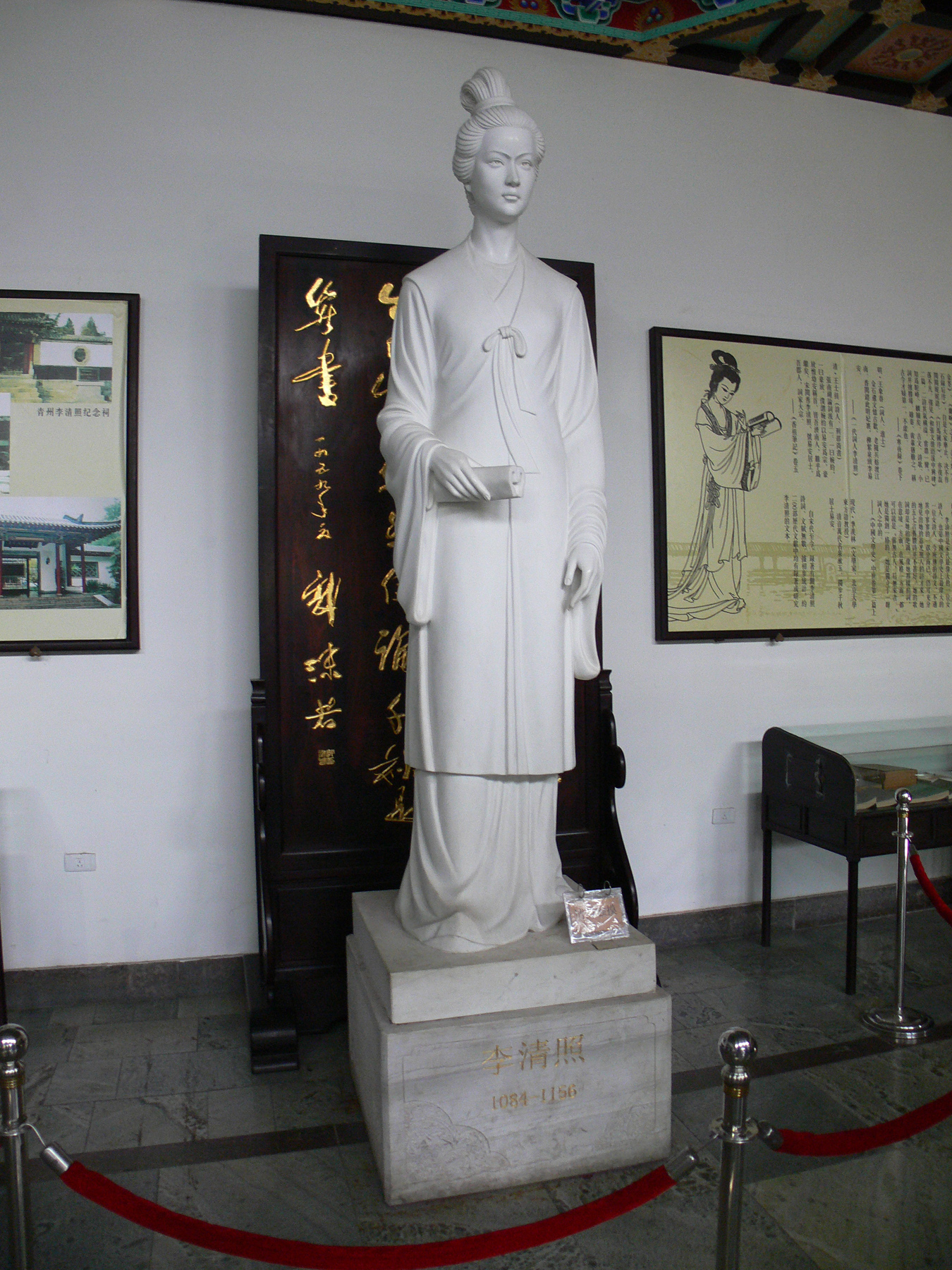
4: Li Qingzhao statue at Li Qingzhao Memorial, Jinan by User Gisling in Wikimedia Commons – Link
The inscription reads: “Li Qingzhao 1084-1156”